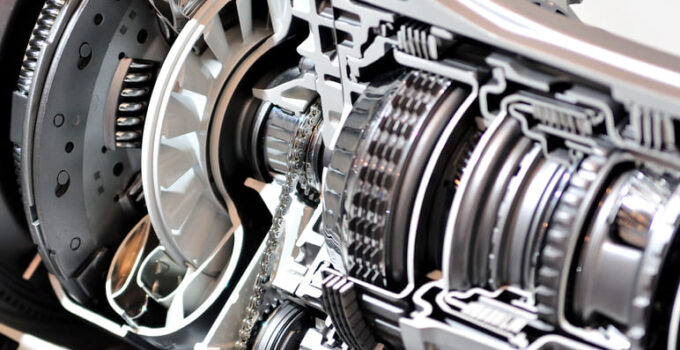
The general function of your clutch is to move the transmission to change gears to disconnect the vehicle engine. This module thus plays an important role in vehicles with a manual transmission. Depending on the vehicle model and variant, the built-in clutch works with the existing 4, 5– or 6 speed gearbox together. The clutch pedal is always depressed when the connection between the engine and transmission is to be separated. This is done by moving the corresponding clutch discs apart. In the following article we will explain the exact structure, the types of clutches and how they work.
Contents
What is the exact task of the clutch in your car
There are a number of functions of a clutch in your car. If you drive a vehicle with a manual transmission, a single assembly is usually installed, while particularly advanced automatic transmissions are even equipped with two clutches. This is also referred to as a dual clutch transmission. In addition to releasing and restoring the transmission-engine connection, the clutch can also ensure that the different speeds of the transmission and engine are balanced. The clutch is also essential for comfortable starting and stopping without having to switch off your engine. As already mentioned, stepping on the clutch allows you to change gear and thus change the gear ratio in order to be able to optimally utilize the engine power in all driving modes.
What types of clutches are there
A clutch type that is particularly common is the modern SAC clutch (self-adjusting clutch). This design was developed because wear and tear on the discs within your car's clutch has a negative effect on their functionality. More precisely, with increasing wear, the required force with which you have to press the pedal increases. SAC clutches are now able to compensate for this with automated wear adjustment. This takes place within the corresponding pressure plate. In this way, you benefit from constant pedal force over the entire service life of the clutch.
As already mentioned, so-called double clutches are also often used in automatic transmissions. There are two coupling connections within a single assembly. These are either so-called dry clutches of the diaphragm spring clutch type or wet clutches. In the latter option, so-called multi-plate clutches are often used, with oil flowing around them. This also facilitates the cooling of this system.
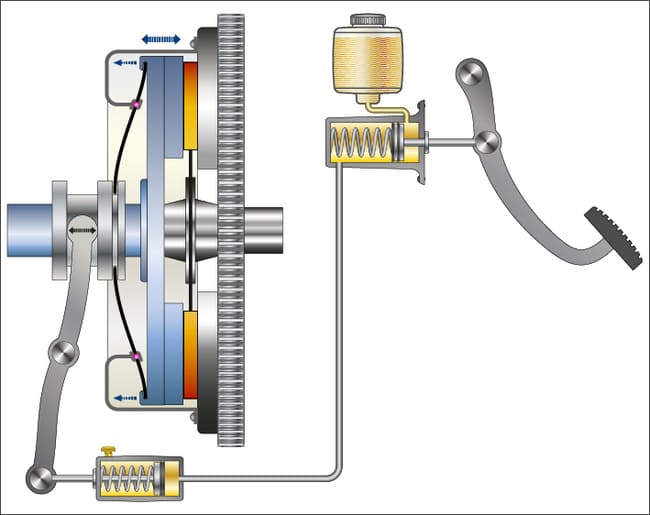
Dual clutch transmissions use the two individual clutches for different gears. As a rule, they are designed in such a way that one clutch is responsible for all odd gears and the other for all even gears. In this way, traction is not interrupted and gear changes can be made particularly quickly.
How is your car's clutch constructed
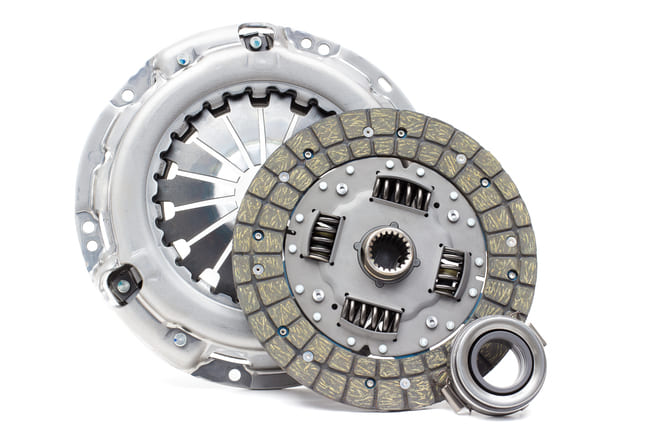

There are several important clutch components. These include the gearbox bell, the gearbox input shaft, the self-adjusting clutch disc, the damped clutch disc, the crankshaft stub, the dual-mass flywheel and the hydraulic release bearing. This structure makes it possible to transfer the engine torque to the transmission via the clutch with almost no loss; at least as long as you don't operate the clutch and thus disengage it. As long as you press the clutch pedal, the release bearing is exposed to high loads. Therefore, you should only disengage your clutch for as short a time as possible and, if necessary, simply put it into neutral.
How does a clutch work
In passenger cars, actuation of the clutch always leads to disengagement of the same. However, this does not always have to be the case, because the opposite is also the case with construction machinery. The clutch may have to be actuated there in order to engage the transmission. With manual transmissions, you use the clutch pedal to generate the impulse to disengage the relevant connection. Depending on the type and clutch design, certain components are non-rotatably connected to your engine crankshaft or to the transmission input shaft. These are normally connected to each other with a non-positive fit and can be separated from each other by the force of your foot.
How long does a coupling last
The service life of a car clutch can generally be classified as very high. So there are many cases where the clutch could be used up to 100,000-200,000 kilometers. But all in all, one has to assume nowadays that this lifespan will tend to shorten. This is due to the increasing demands on this essential assembly. So there are more and more traffic jams because the traffic keeps increasing. These increased loads are also caused by more stop&go, mountain driving, certain traffic light phases and vehicle parking.
However, there are a few ways to significantly increase clutch life. This includes, in particular, not letting your car's clutch slip for too long. Otherwise you would risk the friction lining wear increasing significantly. This, in turn, would result in your clutch no longer functioning properly. If you have to stop at a red light, you should depress the clutch to shift into neutral. It is not advisable to keep the pedal depressed all the time, as this would result in a high additional load on the clutch release bearing.

In order to protect the assembly, it is also advisable to stick to the gear sequence exactly. If you tend to avoid certain aisles and therefore skip them, it's best to hold back. This results in particularly large speed differences, which also puts a strain on the clutch.
Conclusion
The clutch is one of the most important assemblies in vehicles with manual transmissions. So make sure you take good care of them. If you notice that this system is prone to increased wear or is no longer working properly, you should have your car clutch repaired by a specialist workshop. Otherwise you would run the risk of your malfunctioning clutch becoming a safety hazard on the road.
A tip from CarTipsandmore: Because clutch replacement can be very expensive, we recommend that you rather focus on prevention rather than aftercare. We therefore urgently advise you to follow our instructions on how to protect the clutch. With normal use, you can easily achieve a service life of up to 200,000 kilometers.
